What is Task Analysis and How to Use It to Improve UX
Defining the concerns of the users is one of the most significant steps in the Design Thought process and is also used as common practice in UX design. This means being able to define and express customer interface challenges easily enough that you can continue the ideation process later (i.e., generating great ideas on how to solve them). It is not possible to enhance the user experience without a clear comprehension of the viewpoint of the user. In fact, a clear concept of task analysis is that it's a method by which advertisers can catch the thought process behind the actions of users. It is a systematic inquiry into what the customers are trying to do and what they experience when they do it.
- Part 1: What is task analysis?
- Part 2: Two common types of task analysis
- Part 3: How to use task analysis to improve UX?
- Part 4: Software for UX
What is task analysis?
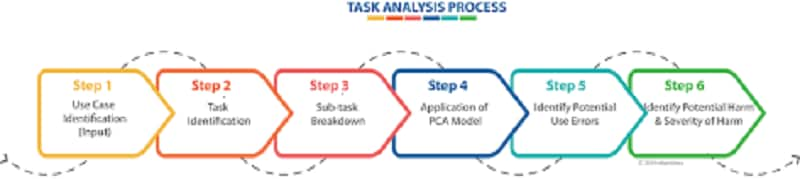
Task Analysis is a basic activity that can be performed by UX designers during the description of an issue and can help not only define where there are possibilities to strengthen the user interface but also create some preliminary ideas on how to solve these problems. App developers and UX programmers are able to dive into the user interface and take lessons to enhance the product by breaking down the most critical user priorities into a set of subtasks.
One of the methods you can use during the "define" step of the Design Thought process is role review. A diagram illustrating the actions a user must take in order to achieve a target is the most common deliverable in a task analysis operation. You may represent the actions taken by the users (or any system) in this diagram to help them accomplish their goals. When you have set out all the steps, you will then be able to see if extra user assistance is needed or to remove redundant steps to minimize the number of unassisted acts a user needs to take.
Task analysis will have a significant effect on the design process on key decisions made. As a consequence, early in the process, it should be performed. When you've been making big design choices, it's surely not something that can happen. Typically, during user testing (which typically occurs in the empathizing and shaping stages of the UX design phase), the task analysis process can start; therefore, the effects of your task analysis should be baked into other core activities in the design process, including obtaining specifications, designing content planning and site layout, wireframing and prototyping.
Two common types of task analysis
There are many forms of job analysis, but cognitive task analysis and hierarchical task analysis are the two styles that are used more regularly.
- Cognitive Task Analysis
The study of cognitive functions relies on learning the cognitive outlay involved in performing tasks. It requires decision-making, problem-solving, recall, judgment, and concentration. For this kind of task review, one of the key things to bear in mind is that the outcomes can differ from task to task, depending on the individual.
A professional user, for instance, will locate a carton of milk instantly and conveniently and put it in an online shopping cart, while this process would take a considerably longer time for a new user. Cognitive task research helps UX programmers to explore how the task is performed for all groups of users and how they can make the task smoother for the new user.
- Hierarchical Task Analysis
The most widely used sort of task analysis is hierarchical task analysis. In order to explain the way the customer deals with a particular product, hierarchical task analysis basically means breaking a task down into sub-tasks. Peter Hornsby of UX Matters states that this will assist UX designers no matter what type of project they are working on a task review helps UX designers to analyze various alternatives to the same task and arrive at the right one when making a new product, and it can help refine interactions and complete the task when redesigning a current product.

Bear in mind that these two forms of task analysis may also be mixed by noting where during the subtasks described in hierarchical task analysis, key decisions or other cognitive factors can come into play. In reality, when analyzing a given task, there are several different items that can be accounted for. Experts include a long list that contains the job context, what causes the task, how long it takes to execute the task, and how much the task is done. They warn that by task analysis, it will be difficult to catch anything that plays a role in a single task, but at least most task analyses can capture the series of subtasks that make up a task and a task summary.
How to use task analysis to improve UX?
Two different steps are used in job analysis: collecting information to classify which tasks should be evaluated and then evaluating those tasks.
- Collecting Data
In role analysis, the first step includes user testing. To discover the main activities users conduct with a product and how they perform them, UX designers can use any one of a multitude of user testing techniques. In this stage, everything from watching a consumer as they perform a task to questioning them can be included. The ultimate aim is to determine the events that should be evaluated.
- Analyzing tasks
After the UX creator agrees on the tasks to examine, it is important to construct different papers that break down each particular task. Although this document may be a basic list or a comprehensive flowchart, a structured task-analysis diagram would most generally take the shape of this document. A sequential task-analysis diagram visually points out the goal of the user, the tasks they need to perform to accomplish the goal, and the subtasks in a visual format that illustrates the order and interaction between these elements that go into each task.

Experts offer a great description of what the job analysis method looks like with a visualization of the task analysis. A task-analysis diagram is helpful in helping the UX creator envision and appreciate the actions a user is supposed to take to accomplish a particular target. This diagram can, though, also be used as a living text that can be changed and updated.
For starters, if the intention of a customer is to make an online grocery store transaction and they wish to reorder something from a prior order, they would have to log in to their account. Any users might forget their password, however, causing them to reset it. The identification of this future step in the task-analysis diagram would be important.
That some UX programmers tend to use spreadsheets over diagrams for job analysis is the need for modifications and modifications, while others use a printed list of tasks in conjunction with a diagram.
Software for UX
Wondershare Mockitt is a leading online collaboration and prototyping forum for websites and apps that lets UX/UI designers produce concept sketches. For someone who enjoys making an app and spending less time learning its simple functionalities, this is a top prototype forum.
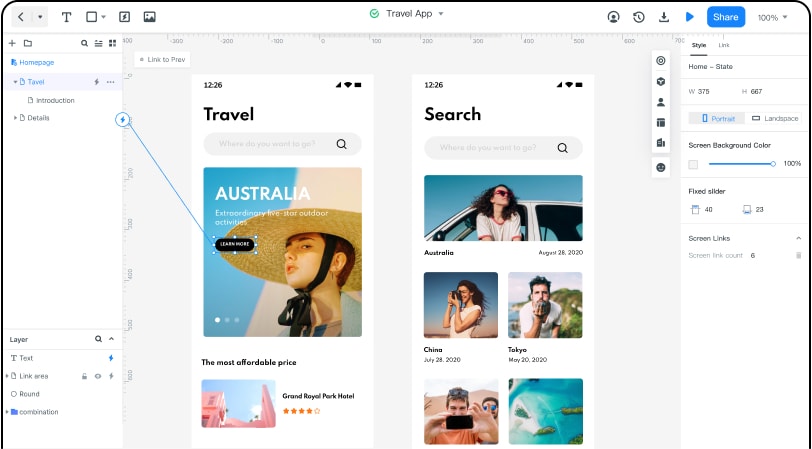
Wondershare Mockitt is committed to novices, casual clients, newcomers, and even seasoned artists. With the instrument, anyone can learn how to build designs irrespective of their ability levels. Its features include:
- Prototyping: There are different repositories rich in models and assets on the web. The library facilitates a seamless creation process for both teams and independent developers. The tool does not disappoint you as a beginner, and it is easy to learn how to begin your project. It is quick to build a project without any previous experience with its uncluttered interface and simple software.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Wondershare Mockitt helps you to communicate with your teammates in real-time, and you can work on the same page to move the transition to higher stages. You will collaborate with someone on the same board to be able to see in real-time the progress your teammates are making. It facilitates transparent collaboration with the members of your team, thereby facilitating a seamless operating process.
- Sketch-Plugin: With this plugin, you can import Sketch Canvas directly to Mockitt. Maintain hierarchical data, allowing designers to build immersive designs that are more refined. Create interactive links by using the "link area" to select the Sketch component and dragging the link line to another page. Use the manual color picker to change automatically generated page colors. Fetch the pixel color value on the current tab.
